Micro Arc Joining for Electric Vehicle and Battery Applications
AMADA WELD TECH shares expert insights into technology that offers mechanically robust and electrically conductive joints.
Posted: September 2, 2024
Micro Arc Joining uses the thermal energy generated by a current arcing across an arc-gap, to melt and join conductive materials together. The technology is prized for its inherent capability to join conductive and dissimilar materials without solder and is also known as Micro TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding, GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding), or Pulse Arc Welding. The resultant joint is both mechanically robust and electrically conductive, making it an excellent choice for electric vehicle (EV) applications, particularly e-Axle drive units, coils, and batteries.
Micro Arc Joining Under the Hood
Micro TIG is an arc welding process that creates a high‐temperature (5,000°C) plasma arc between a tungsten electrode and the work piece. An inert gas (typically argon) helps plasma arc generation by displacing air from the weld area, thus lowering the resistance or voltage requirement to jump across the gap.
The technology is geared toward weld areas that are <18mm2, for example a copper busbar, and reaching spots as small as 0.14mm2, for example, 2 thermocouple wires. This is achieved by supplying a lower current for shorter times and with more precise control.
Micro TIG welders typically supply a current from 5 to 300 Amps with pulse durations of up to 999ms. Sometimes the pulse is divided into multiple pulses by rapidly turning the current on and off. This feature, called “current modulation”, reduces the porosity of the completed weld nugget.
By heating metal material through the arc formation, Micro TIG welding causes materials to melt and fuse together. The best results come from joining two pieces of the same metal of similar size. However, it is also possible to weld dissimilar metals.
Which Materials?
Good materials for Micro TIG Welding include copper, phosphor bronze, iron, nickel, stainless steel, molybdenum, tungsten, platinum, and titanium. Brass and galvanized steel are not considered appropriate for Micro TIG welding, because their zinc content causes welding issues such as porosity and soot contamination.
Applications of pulsed Micro TIG Welding include battery tab welding and coil wire welding.
Micro TIG welding has many advantages. As a solder-free process, the resultant weld is highly durable when exposed to vibration and heat. In addition, pulsed Micro TIG welding is widely applicable for joining high melting point metals, dissimilar metals, and even thin magnet wires of φ0.02mm.
Micro TIG Welding Technologies

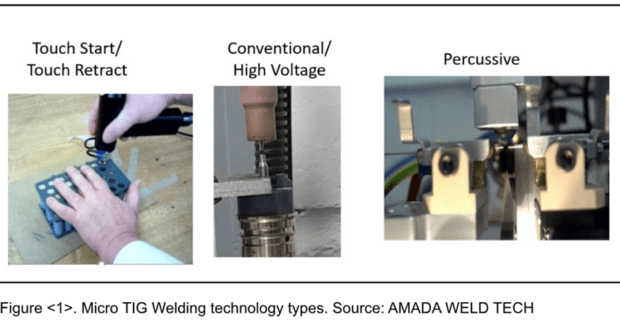
Different Micro arc Joining technologies are suitable for different applications and/or process requirements. The three most common use a touch-start mechanism, high-voltage start mechanism, or a percussive process. See Figure 1.
Touch-Start
If a touch-start mechanism is used, the electrode comes down to touch the workpiece and then retracts, causing an arc to be generated. The weld area is generally protected from atmospheric contamination by use of an inert shielding or cover gas (argon or helium).
High-Voltage
With a high-voltage start mechanism, the standoff between electrode and workpiece is set at a fixed distance. The start arc must then overcome the breakdown of air to bridge the gap.
Percussive Arc Welding
Percussive Arc Welding combines Micro Arc TIG welding with a mechanical “percussive” movement that forces the arcing components together. The heat from the arc creates two molten interfaces which, when pushed together, fuse as a weld and extinguish the arc, forming a butt weld. The process is very quick and controllable and, as such, requires high-speed real-time control elements and a degree of programmable flexibility to deliver a manufacturing standard system. It is widely used for butt welding of thin wires, stranded wire to pin joining, and blind thermocouple welding.
Application Examples
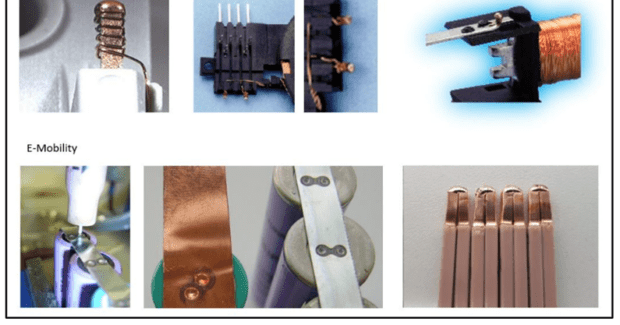
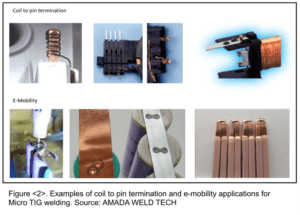
Examples of Micro TIG Welding used for typical coil to pin termination and E-mobility applications are shown in Figure 2.
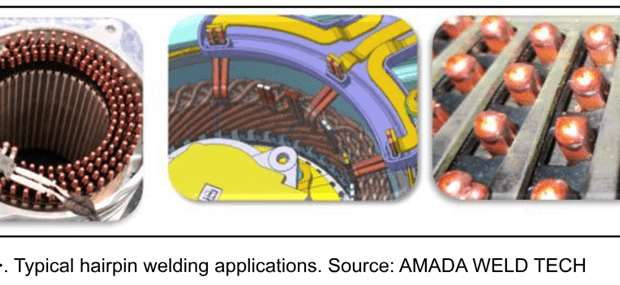
Hairpin Joining
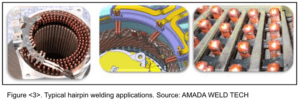
One of the most common applications is hairpin joining, which is being used more and more as manufacturers seek to build smaller, lighter, more powerful electric motors that improve electro-conductivity. See Figure 3.
With Micro TIG Welding, accessibility to the weld joint is from the top of the hairpins, making it a good process to consider when there are space constraints. Alignment of the pins is key to getting a good weld. The pins and torch need to be precisely aligned such that the centre of the torch is positioned in the middle of the pins. Tooling is required to achieve precise and repeatable alignment; this will result in symmetrical weld geometries.
Micro TIG Welding Equipment Selection
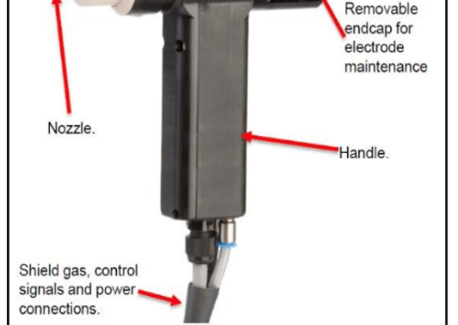
Equipment selection is key to successful Micro TIG Welding. One option is AMADA WELD TECH’s Touch Retract System, which includes the TR-T0016A Touch Retract Micro Arc Torch paired with the PA-T0200A Power Supply.
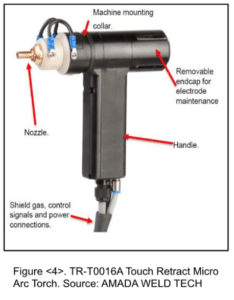
The Touch Retract Micro Arc Torch works like a hand-held tool, which allows staff to use the torch after a short training to rapidly assemble prototype technologies such as battery packs. See Figure 4.
The welding process proceeds in three steps:
- Approach: The electrode extends below the nozzle, enabling the operator to see where they are placing the weld.
- Compression: During the compression step, the operator pushes down on the torch. A small current detects that the electrode is in contact with the workpiece.
- Retraction: In the final retraction phase, the electrode retracts, drawing an arc with an intermediate current. When the mechanism is at full travel, the main welding current is applied.
The torch offers a machine mounting collar for integration into automated solutions. A 7mm nozzle and protruding electrode leads to easy location of the weld area and it includes an integral ground contact for arc operation and welding gas discharge port. There is no user contact with components at high voltage and no direct exposure to artificial optical radiation.
For scaling up production, the TR-T0016A Torch can be mounted on automated production solutions for uniform and high-speed production. See Figure 5.

The high degree of control offered by the PA-T Power Supply enables the resultant spot welds to be size-optimized while minimizing battery can heat penetration. The power supply includes an intuitive colour touch screen, I/O, configuration and calibration screens, a built-in weld counter, and a graph of voltage for last weld and energy trend against time. It is fully programmable, with upslope, peak and downslope. Current modulation allows the user to selectively turn the current on and off during the weld. This results in controlled heat input to the part, eliminates internal porosity and external dimples, and makes the weld size and shape uniform.
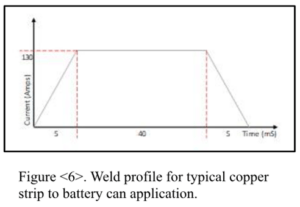
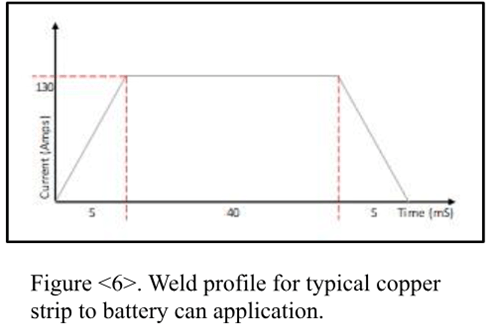
For example, a typical 0.3mm copper strip to 18650 battery can application will require the a weld profile as shown in Figure 6.
The Touch Retract system has a duty cycle rating of 5 percent at 100A. For a weld with the profile shown, this equates to a maximum work rate of a single 50mS pulse of 100A per second, or a weld about every 1.3 seconds.
For percussive arc welding for on axis stranded wire to pin terminations, a good power option is the Percussive Arc Power Supply PA-P200A. This 200-amp percussive arc linear TIG welding power supply incorporates power electronics, interfacing and software to facilitate highly controlled percussive arc processes to be performed with a high degree of process control, monitoring and checking.
Summary
For EV manufacturers looking for mechanically robust and electrically conductive joints, Micro TIG Welding can be an excellent choice, particularly for battery call/busbar assembly, sensor joining, and connector joining, as well as automobile coil, busbar, solenoid, harness, and sensor applications.
About AMADA WELD TECH
AMADA WELD TECH is a leading manufacturer of equipment and systems for Laser Welding, Laser Marking, Laser Cutting, Resistance Welding, Hermetic Sealing and Hot Bar Reflow Soldering & Bonding. We design and manufacture industry-leading product families for the global market and customize our products around specific micro-joining applications. AMADA WELD TECH’s key markets include medical devices, battery, automotive, solar industry, electronic components and aerospace. AMADA WELD TECH Europe is headquartered in Germany and has additional production facilities in The Netherlands and UK, as well as sales offices in France, Hungary and Italy and part of the global AMADA Group, with over 8.500 employees worldwide. More on products and services: https://www.amadaweldtech.eu/.