Welding’s Transformation: From Digital to AI
How technology is transforming training, learning and work in manual welding, cobots and automated systems.
Posted: August 22, 2024

The welding industry has been embracing an era of technological innovation led by advanced manual welding equipment, collaborative robots (cobots) and fully automated industrial robotic systems — the combination of which is reshaping the way welders and operators learn, train and work. The latest tools are not only enhancing productivity, but also streamlining the educational process for those entering the field as well as seasoned professionals.
From the classroom to the factory floor, the latest welding equipment allows operators to accelerate skill acquisition, refine welding techniques and optimize performance. What’s more, these tailored solutions cater to the unique demands of each operation’s size, output and footprint. Modern welding technologies are ensuring the workforce is equipped to meet the challenges of today’s manufacturing environment with unparalleled efficiency and precision.
Manual Welding
In today’s welding market, where operator shortages and tight production schedules are a daily concern, technology is filling gaps in education and labor. Augmented reality (AR) can swiftly train new welders, while advanced manual welding technology in the field helps boost learning while also furthering efficiency and productivity.
AR simulators are accelerating the education process, giving beginner operators practice at MIG, TIG and stick welding before working with real materials and without the risk of heat and sparks. Through an AR helmet, users see computer-generated 3D images of metal workpieces and “weld” them with the system’s gun and torch. Offering real-time feedback on factors like contact tip to work distance, travel and work angles and travel speed, AR can accelerate the learning process and appeals to digital natives, allowing welders to develop skills and muscle memory while conserving coupons and consumables. Manufacturers also recognize their value for recruitment, job proficiency assessments and skill enhancement.
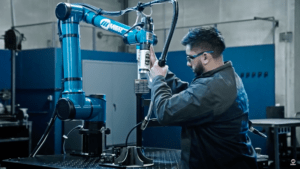
The latest welder equipment, which now features intuitive interfaces and controls, offers even experienced operators the ability to gain efficiencies and expand technical knowledge. Modern welders’ digital displays can offer immediate parameter feedback — including wire feed speed, arc length and travel speed. This allows welders to see how their technique deviates from the ideal so they can adjust accordingly in real time. These instruments can also record detailed data from each welding session so operators and supervisors can pinpoint areas for improvement and focus on enhancing key skills to boost productivity.
The newest welding machines have been engineered to incorporate sophisticated sensors capable of detecting and autonomously correcting errors. For example, self-adjusting arc lengths can sustain ideal welding conditions — not only elevating the quality of welds produced by learners, but also underscoring consistency and precision in welding practices. Additionally, they can record intricate data from each welding session — which gives welders, supervisors, instructors and students information so that they can pinpoint areas for improvement.
Preset and automatic capabilities are leading the field in today’s manual welding landscape, facilitating operator productivity whether learning or on the job. Features and benefits include:
- Self-adjusting arc lengths detect and adjust settings to correct errors, elevating the weld quality, consistency and precision.
- Cable length compensation ensures actual voltage matches the display regardless of the distance between the power source and the welding location, supporting efficiency in the field.
- Connection and communication between the welder and power source allow the operator to adjust settings without the need to stop welding, walk to the power source, make manual adjustments and return to the site of the weld. This saves hours over the course of a year, enhancing productivity.
- Displays with more intuitive visual cues make interfaces easier to use, including cut-and-paste, click-and-drag and symbols that represent program elements and touch screens.
In addition to serving today’s welders, progress in welding technology and education is empowering the next generation of operators with enhanced capabilities and sets a new standard for the industry’s approach to training and skill development that facilitate work and boost productivity.
Cobots
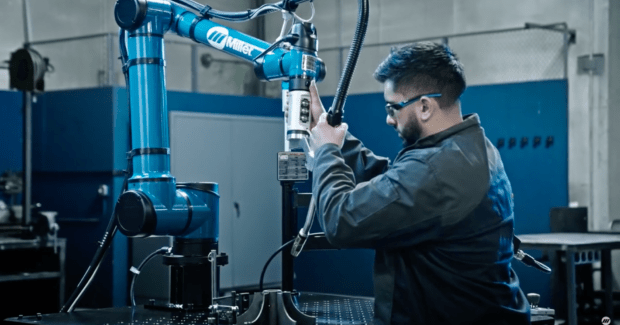
In the welding industry’s ongoing journey toward efficiency, collaborative robots (cobots) are a leap forward. These user-friendly entry points to automation help shops safely and easily integrate operator-assisted robotic systems. Cobots are ideal for low-volume, high-mix part production, which provides flexibility that robotic setups can’t match. While their operational speed may not rival that of full automation — owing to the human element — cobots’ design compensates for it, prioritizing ease of use and rapid reconfiguration for different tasks. Cobots’ small footprint makes them easily transportable and easy to integrate on a shop floor, safely — fitting into the same footprint as a manual weld cell. They’re also approachable to use for new and seasoned welders alike — helping broaden the talent pool and empowering existing welders to elevate their craft.
The intuitive programming of cobots drastically reduces the learning curve, allowing operators to swiftly adapt to various parameters. Straightforward settings enable welders across the spectrum of experience to achieve high-quality welds with consistency and speed, minimizing downtime. This allows veteran welders to dedicate their expertise to more difficult projects as cobots and their operators manage the routine tasks, alleviating pressure in often understaffed environments. Additionally, the user-friendly nature of this type of machine is particularly attractive to digital natives in the workforce, aligning with their affinity for technology and enhancing the safety and accessibility of welding as a career path. Women are also more likely to be interested in automation-based welding versus manual computer-assisted welding according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Overall, cobots are demystifying the welding process. They present a less daunting entry point into the industry compared to a longer on-ramp to productivity in manual welding — and offer a more affordable and approachable shop integration within the automation spectrum.
Robotic Welding
At the vanguard of welding automation, robotic welding systems are proving to be indispensable for operations with high-volume, low-mix production. These systems deliver speed, precision and the consistently exceptional welds required in high-stakes manufacturing environments where productivity is paramount. Suited for complex applications and expansive workspaces, these automated setups require a greater level of operator expertise to integrate and manage. They also demand weld cells with dedicated floor space to maintain the precise programming needed to achieve repeatability over the course of the run. Industrial robotic welding cells are designed to complete tasks independently, so extensive safety measures are required to keep operators at a safe distance on the shop floor.
The intricacies of robot programming, joint geometry and specific weld parameters call for a more comprehensive educational background and training. That said, technology in industrial robot pendants borrows from the cell phone industry. The accelerometers that detect changes in cell phone position and then trigger shifts to the orientation of the display are being introduced to robot pendants to provide a new, perhaps more intuitive, means of a user interface. This allows for a new way to teach the robot that’s familiar and approachable for operators.
The strategic integration of robotic welders within the workforce not only enhances adaptability but also significantly boosts productivity. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of automated welding solutions becomes increasingly central to the future of manufacturing excellence.
The Future of Learning, Training and Productivity
The welding industry stands at the precipice of a transformative age, one where a blend of human skill and robotic precision will together forge the future of manufacturing. Welding machine advancements, cobot adoption and robotic welding system integration reflect the tapestry of the industry’s technological progress, and innovations across these spheres are building a landscape of intuitive learning, more efficient training and greater productivity. All of this is critical given how much welding work is out there to be done and the shortage of workers the industry is striving to fill.
Meanwhile, welding manufacturers are also researching how AI can and will enhance welding technologies. AI now has the ability to record the habits of human operators and may soon be able to quickly program itself using simple, task-oriented instructions paired with part design and workpiece information. It’s possible that AI will transform high-level task descriptions or visual demonstrations and generate the information into code, further simplifying the process and deploying systems. Harnessing the combination of AI, the IoT (Internet of Things) and real-time, high-speed communications and sampling with the cloud has implications for process monitoring and quality control that will create a new state of the art for welding productivity and competitiveness.
Looking to the horizon, it’s clear welding manufacturers are working to equip operators with the machines and welding technology they need to excel in an increasingly competitive global market — thinking beyond the current benchmarks of quality, safety and efficiency to meet the demands of tomorrow with confidence.