The AMADA Global Innovation Center: Unlimited Opportunities to Shape the Future of Fabrication
The new cutting-edge AGIC empowers fabricators to embrace the “why is this possible,” beyond the “what is possible,” regarding metal fabrication machinery and solutions.
Posted: June 15, 2023

Imagine metal fabricators gathering in one inspiring facility, collaborating with engineers to co-create the future of the metalworking industry. Picture a venue that encourages fabricators to explore new shapes, experience the promise of emerging sectors such as electric vehicles and new processes in aluminum, as well as utilizing materials yet to be developed — the possibilities are infinite.
Visualize an innovation center that fosters an environment of collaboration that will result in the creation of leading-edge processes driven by digital transformation, as an example. A place where companies can come to understand the “why is this possible” rather than “what is possible” regarding advances in fabrication machine technologies. A location where a guiding factor in the evolution of these technologies addresses social issues such as the implementation of carbon neutral initiatives, and ways to overcome skilled worker shortages through automation solutions, artificial intelligence (AI) and digital experience (DX).
Such a dynamic environment officially opened its doors in February of this year in Isehara City, Kanagawa, Japan. The AMADA Global Innovation Center (AGIC) is a state-of-the art facility where AMADA engineers and customers can collaborate, develop and verify new processes in the metal fabrication industry. The AGIC has two functions: to “challenge future processing technology by verification”; and “creating a center where customers can experience the value they expect, as well as the latest technologies.” The AGIC facility has earned Science-based Targets Initiative (SBTi) certification to support research and verification.

In April of this year, AMADA CO., LTD., a leading global sheet metal fabrication machine business, opened the doors of the AGIC to media from the United States and Europe to learn all about this newly expanded, environmentally friendly innovation center (an engineering/research center in its third iteration) that features nine one-of-a-kind labs designed to inspire the future of metalworking. The AGIC offers a variety of functional areas where AMADA can continue the company’s philosophy of “growing together with our customers.”
In a press conference held on April 19, AMADA’s leadership spoke of how the AGIC is a cornerstone to AMADA’s future. Eighty percent of the products displayed inside AGIC are newer products that will contribute to solving societal and environmental issues by manufacturing new technologies, noted Tsutomu Isobe, representative director and president, AMADA CO., LTD. The company will work with customers to deal with challenges through innovation and address concerns such as:
- The environment, where electric servo drives on AMADA’s machines, and idling functions on chillers and compressors result in decreases in CO2 emissions, as an example).
- Easy to use machinery using face recognition interfaces and human-machine interfaces (HMI) (see sidebar “The Evolution Continues: AMNC 4ie”) as well as automated products.
- Developing new activities by shifting to new sales, service, and manufacturing by utilizing DX.
Exceptional Top-quality Capabilities: Innovation LABO and Innovation SITE


Among the numerous areas within the nearly 32,2917-square-foot AGIC, major highlights are the Innovation LABO and the Innovation SITE sections. The services at AGIC are offered at no cost to AMADA’s customers, who can collaborate with AMADA’s engineers; AMADA supplies the majority of the materials for testing. Companies can also bring their own components to test. Companies enter into nondisclosure agreements before they collaborate at the Innovation LABO.
Before visitors arrive at the Innovation LABO they are welcomed with a video at the entrance of AGIC that outlines ideas and concepts they will experience, including the “4-I’s” that comprise the new AMNC 4ie unit: intelligent, innovative, interactive and integration.
Visitors then move to the Future Vision Room, an interactive, multiscreen room that highlights the history of AMADA and its role in the metal fabrication industry, as well as the evolution of fabrication technology, such as the move from mass production to high mix, low volume fiber laser machines to the importance of eco-friendly machines and artificial intelligence for today and the future. Visitors learn the concepts behind the creation of AGIC, as well as AMADA’s philosophy of “growing together with our customers.”
Visitors then move to the heart of the AGIC. First stop are the nine labs that comprise the Innovation LABO, the sheet metal fabrication industry’s first such lab. Labs focus on research in fiber laser welding; standalone press brakes; bending automation; lasers; a laser and punch combination room; robotics; and a €1 million EUR measuring room to verify research. Lab spaces are secured through identification systems so that verifications for blanking, bending, and welding processes can be conducted with confidence. The Innovation LABO is AMADA’s answer to “challenge future processing technology by verification.”

Moving to the Innovation SITE, which is located across from the LABO area, users experience the second function of AGIC, where “customers can experience the value they expect, as well as the latest technologies.” Throughout the media tour in Isehara, AMADA’s leadership continued to express the importance of “why it can be done” beyond “what can be done” regarding advances in fabrication machine technologies.

“Addressing the why of the technology — this is a fundamental change,” said Matt Wood, EU Product Marketing (Blanking) Manager, for AMADA United Kingdom Ltd. When customers understand the mechanisms and structures behind the technology, they can better embrace the “why” a certain process is possible.
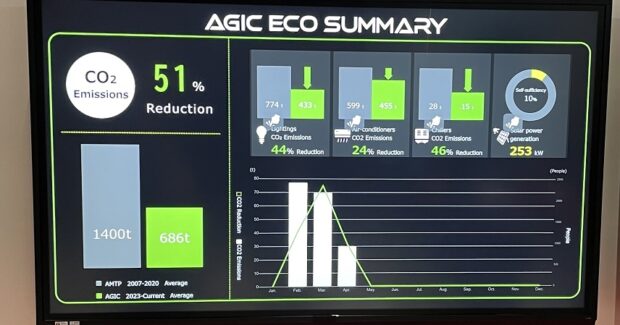
The entrance to the Innovation SITE features two interactive displays that demonstrate in real time AMADA’s commitment as a manufacturer to protecting the global environment. The ECO Dashboard monitors the status of the processing machines on display and at work in the Innovation SITE, and how they are using and saving energy, which includes tracking CO2 emissions. An AI-number judging system monitors the number of people visiting the site to adapt air conditioning and lighting usage. Energy saving components include idling stop functions on chillers and compressors on machines.
Additionally, the ECO Summary Dashboard, among its capabilities, explores in detail the reductions of CO2 emissions occurring at the AGIC overall. It also displays the solar power being generated at any given time. The solar panels at AGIC generate approximately 11% of its total electric power.


In total, the environmentally friendly initiatives at AGIC will reduce CO2 emissions by 700 tons per year, equaling a 50% reduction in CO2 generation compared to the previous iteration of the facility.
Moving to the core of the Innovation SITE, visitors can access first-hand the more than 90 fabrication machines and technologies on display. They can explore the mechanisms and structures (the “why”) of the machines to better understand the functions and processes. There are six process zones in the Innovation SITE, each featuring the latest machines, some with electric servo drives, and automation technologies to solve the challenges of today and tomorrow. The process zones are split into two sites. Site 1 is comprised of the Laser Zone, the Welding Zone and the Punching & Combination Zone. Site 2 is comprised of the Bending Zone, the Press Zone and the Machinery Zone. Each zone features a Technical Corner to further explore manufacturing processes, “the why is this possible” with AMADA’s engineers.
In addition to the emphasized Innovation LABO and Innovation SITE areas of AGIC, additional areas include support, conference rooms and gathering areas to enhance the visitor experience.
One room that instantly promotes inspiration is the Precision Sheet Metal Technology Fair. The fair showcases AMADA’s commitment to the development of a better society through manufacturing innovation and cutting-edge ideas. AMADA has operated the fair for 35 years with the support of the Japanese government and industry associations to contribute to the development of the sheet metal fabrication industry. Each year, engineers submit sheet metal projects to the fair to demonstrate their technical know-how and creative uses of the latest in fabrication technologies.
Another feature at AGIC is the Engineering FIELD, which extends to processing, machinery, and software to support customers’ improvements to their factories and operations. The Innovation SQUARE provides a space to learn more about AMADA’s advanced technologies and experience the spirit of “monozukuri” (manufacturing) via the 75-foot long LED screen, one of the longest such screens in Japan.
Related facilities located near AGIC at the AMADA campus in Isehara include the AMADA Museum, which opened in 2018 in honor of AMADA’s 70th anniversary. The AMADA FORUM serves as a multi-purpose training facility and hotel for customers and visitors.
{Sidebar}
The Evolution Continues: AMNC 4ie
AMADA’s numerical control has evolved to its fourth generation, which will be available in North America in the fourth quarter. The AMNC 4ie’s capabilities are AMADA’s response to social and environmental issues facing the sheet metal fabrication industry, such as shortages of skilled workers and decarbonization initiatives.
The 4 i’s represent: intelligent, interactive, integrated and innovation. The 4 e’s represent: easy, efficiency, environmental and evolution.
The AMNC 4ie unit was at work on select fiber laser machines and bending machines located in the Innovation SITE at the AMADA Global Innovation Center in Isehara City, Japan. AMADA CO., LTD. invited media from the United States and Europe to tour the AGIC in April of this year.
“The AMNC 4ie is a very easy to use processing machine,” said Yoshi Yamaguchi, overseas engineering support dept., AMADA CO., LTD., during a press conference held on April 19. “Even novice operators can operate and utilize the machine. That is what we were aiming at and working on [during] development.”
Yamaguchi explained one of the control’s advantages in addressing workforce issues with the example of factories that may have a workforce comprised of workers from different countries. The facial recognition component of the control unit identifies individual operators qualified to work on a specific machine, displaying the proper language for each operator. A machine’s screen is easily switched over for ease of use by multiple operators.
The AMNC 4ie also enables program-less functions, and easy startup and inspection, including a second monitor to check for errors.
On fiber laser machines, the AMNC 4ie automatically adjusts chillers and compressors while idling, reducing CO2 emissions by up to 65%. Operators can create emissions reports, which can be shared with business partners. Also, with the control, during blank processing, automatic recognition by a camera makes for effective use of scrap by auto shape detection of the scrap and nesting.
When it comes to efficiency, remote monitoring is available with a mobile human-machine interface (HMI), which results in the reduction of onsite manpower because one operator can monitor and run multiple units, which increases productivity levels, noted Matt Wood, EU Product Marketing (Blanking) Manager, for AMADA United Kingdom Ltd. on a tour of the Innovation SITE.
The HMI function also supports maintenance guidance. For example, regarding the nozzle, a user can transfer a maintenance command to a mobile device with a QR code, which indicates the lens needs to be cleaned, as an example, Wood said.
On bending machines, alerts and work points are displayed in conjunction with the process for ease of use. The control’s HMI follows the operator and advises them through displays of icons and voice commands when an operator is performing difficult or dangerous tasks. Users can easily hit the bend target by aligning with the display.
Subscribe to learn the latest in manufacturing.