Optimized Tooling and Workholding Help Aerospace Machine Shops Stay Competitive
Innovative tools improve productivity and process security, specifically when working with titanium and HRSAs.
Posted: January 31, 2022
Some aerospace components manufactured by machine shops can cost tens of thousands of dollars apiece. While tooling these may seem like pressure enough, consider that the heat-resistant super alloys (HRSAs) these engine components are made from are incredibly difficult to machine. Shops must ensure processes are highly secure to keep from scrapping workpieces, yet fast enough to meet demand. The tools that shops use can significantly affect their success.
To remain competitive, aerospace machine shops need innovative tools that improve productivity and process security, especially when working with titanium and HRSAs. The latest advancements in aerospace machining technology, such as optimized quick-change systems and toolholding, can stabilize set-ups, improve machining accuracy and reduce cycle time when manufacturing aerospace engine components.
Greater stability and precision
Aerospace engine components have strict tolerances. Each feature must be accurately machined and uniform from workpiece to workpiece. To achieve this, the chucks used to stabilize tools and workpieces in aerospace milling and drilling operations must hold them securely in precise alignment.
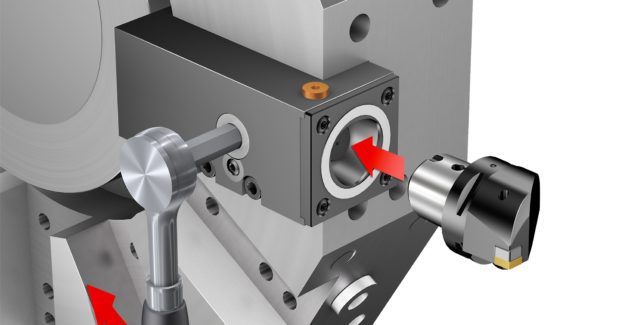
New fulcrum technology in hydraulic chucks provides greater clamping forces, resulting in a stable and secure process while using solid round tools. A distinct, brazed membrane sets these chucks apart. The unique design includes two supports, or fulcrums, on each side that offer highly secure clamping and prevents tools from pulling out. These chucks also hold tolerances within microns and are designed with damping features that further minimize vibrations during the machining process. Such a high level of precision can improve repeatability, surface finish, tool wear and productivity.
In addition to providing greater stability and precision, these chucks are also designed to simplify setups and tool changes. A torque wrench can quickly tighten or release the tools; no additional heating equipment is required to clamp or unclamp them.
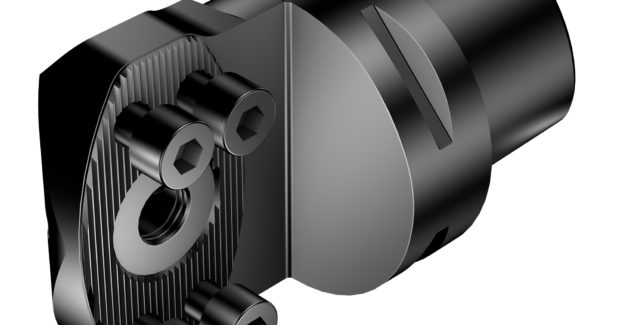
Chucks aren’t the only tool holders that improve stability. Tool holders and inserts with rail interfaces offer secure machining for profiling and pocketing applications. Traditional round inserts tend to move in the pockets during these operations, especially when machining HRSAs. To prevent this, the rail interface locks the rotation of the insert.
Faster, more accurate processes
From roughing to finishing, there’s a lot of machining that must be done before a workpiece is ready. If tool changes are too long or complex during any process, it not only reduces the number of components that can be produced, but it can also introduce a margin of error.
Modular, quick-change tool-holding systems make it possible to reduce setup time, which increases machine utilization by getting aerospace parts out faster with greater accuracy. Advanced quick-change tooling concepts can even make it possible to reduce the steps it takes to machine a component. Reducing the number of steps significantly cuts time and minimizes the chances for an error to occur, ensuring a more secure process.
For aerospace engine components, it’s important to look for a modular system that enables you to build longer tools with standard articles to the length that suits your application and machine tool needs. Different types of adapters are available. For example, Coromant Capto® with SL70 blades are ideal for machining the deep, difficult-to-access pockets commonly found on aerospace components such as engine discs and spools. The blade system provides stability and accessibility while delivering coolant to the cutting edge, improving tool life and chip control.
New grades and geometries optimized for HRSAs can also improve productivity through increased machining speeds. One new carbide turning grade is a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grade that enables up 30-to-50 percent higher cutting speeds in semi-finishing and finishing applications without compromising tolerances or surface integrity. This turning grade can also extend insert life, which means less indexing, better quality parts and increased productivity. Cubic boron nitride (CBN) grades paired with optimized geometries can also be used for finishing nickel based HRSAs at higher speeds.
Optimized solutions for aerospace machining
Successfully tooling aerospace engine components requires machining technology engineered specifically for titanium and HRSA materials. Shops can stay competitive by selecting optimized tools. Quick-change tools and chucks designed to improve process security and productivity help ensure aerospace components are of the highest quality possible.