5G Adaptive Process Control with Extremely Short Reaction Times
Developed by GF Machining Solutions and their partners, this networked adaptive manufacturing system for real-time process monitoring uses 5G technology to communicate with sensors and machines in under one millisecond and reduce errors in high speed machining of complex aerospace parts.
Posted: May 31, 2019
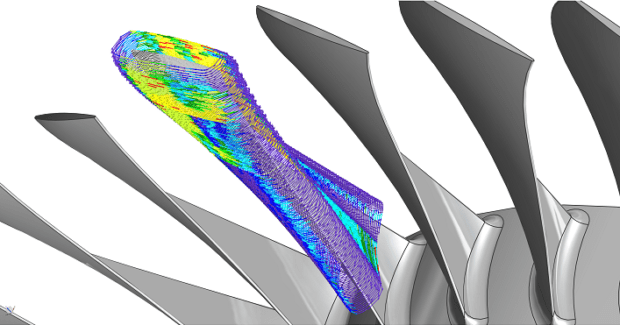
High speed milling of parts can create excessive vibrations that result in surface defects and rework. The aerospace sector requires high process reliability and strict compliance with no room for these errors, so the Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology IPT (Aachen, Germany), Ericsson (Stockholm, Sweden) and GF Machining Solutions (Schaffhausen, Switzerland) have combined their expertise in telecommunications and manufacturing to build a networked adaptive manufacturing system for real-time process monitoring based on 5G technology that communicates with sensors and machines to reduce errors in milling operations used for jet engine production. The ultra-low latency and reliability of Ericsson mobile communications enable increased predictability, real-time monitoring of sensor vibration data and better production control for adjustment of cutting parameters. Wired or unlicensed systems (such as wireless LAN) cannot meet the demanding speeds necessary for this application, but 5G has proven to be the only communication standard that can deliver sensor and production data in under one millisecond.
To further develop these kind of wireless sensor connections for real-time data analysis and ensure adaptive control of production processes with extremely short reaction times, a Mikron MILL P 500 U from GF was selected that uses highly dynamic direct torque motors and a precise gantry with up to 1.7 g acceleration and accuracy of ±2 μm in the plane to deliver the power and precision necessary for such fast reactivity. The manufacture of complex, high precision aerospace components under high safety regulations and standards was identified as a potential early adopter of 5G networks in production. Other sectors are sure to follow as industries switch to more data-driven and flexible manufacturing. Industry 4.0 will rely on increasingly fast, secure and often wireless data transfers to optimize operations, increase automation and mitigate risk in manufacturing environments.
When machining Blade-Integrated Disks (BLISK), a component of a jet engine compressor, the workpiece could not be inspected until the lengthy milling process was over, leading to defective products and rework up to 25 percent. By using 5G enabled process monitoring, a single factory could see annual savings of up to $30 million. “Our main challenge is the increasing number and complexity of parts we have to design and produce. 5G will bring a very important benefit so we can handle more data in real-time,” said Thomas Dautl, the director of manufacturing technology and industrialization at MTU Aero Engines (Munich, Germany). All production and sensor data can be stored individually for each product, creating digital twins for quality design, accurate documentation and analytics. If defects arise, the data pinpoints to where the fault originated and the production can be optimized.
“The interoperability and limitless capabilities of this technology make it a perfect fit for our current analytics-based in-process development and a great enabler of our digitalization road map,” noted Benoit Defrasne, the head of marketing and product management milling at GF Machining Solutions. The potential fields of applications and use cases for 5G are numerous. “We invite all interested companies to visit us in Aachen to experience our unique test environment for industrial 5G applications,” added Niels König, the manager of the production metrology department and coordinator of 5G activities at Fraunhofer IPT. “The International Center for Networked Adaptive Production (ICNAP) in Aachen will gather partners from the ICT and manufacturing industries as a collaboration platform to address all relevant questions that come along with the digitalization of production in the context of Industry 4.0. 5G is currently one of the major topics for ICNAP.”
The selected communication standard determines the type of application, the quality of the data and whether or not machines, sensors, robots can be securely managed and interconnected through one network. “Cellular networks like 4G/LTE and the evolution to 5G provide one simple, secure and smart wireless system for critical and massive IIoT, handling growing network, data and application demands of Industry 4.0,” explained Erik Josefsson, the head of advanced industries at Ericsson.
For more information, look at other advances in the smart factory and also subscribe to F&M.
GF Machining Solutions LLC, 560 Bond Street, Lincolnshire, IL 60069, 847-913-5300, Fax: 847-913-5340, www.gfms.com/us.