Well Handled Operations: An Easy Path to Profitability
Shops are revisiting the use of material handling robots or human-collaborative robot (cobot) utilization for fulfilling diverse tasks with efficiency and accuracy – two things that are sometimes hard to find in human workers because of the growing skills gap.
Posted: November 30, 2018
The current economic climate is generating incentive for manufacturers to build more products in the country where they will be sold. This, combined with more affordable and sophisticated robotic technology, is driving an uptick in automation usage. Companies are realizing that investing in more capital equipment to increase accuracy, quality and productivity is a logical next step to build a competitive edge and achieve organizational success. Depending on the application, optimizing production in this New Year may greatly depend on the implementation of peripheral technologies that enable easier deployment of automation systems. Technological advancements, such as smart pendants and vision systems, are effectively helping companies deal with production inefficiencies while increasing throughput for a simple path to profitability.
Moreover, end user demands are becoming more complicated, encouraging manufacturers to go back to the drawing board and brainstorm unique ways to maximize their workforce and valuable workspace. For this reason, decision makers are revisiting the use of material handling robots or inquiring about human-collaborative robot (cobot) utilization for fulfilling diverse tasks with efficiency and accuracy – two things that are sometimes hard to find in human workers because of the growing skills gap:
- The Use of Material Handling Robots for Press Brake Operation. Often overlooked for certain stages of production, handling robots are reliable, even for harsh environments. From small to large parts, powerful material handling robots are ideal for tasks like press brake applications. The overwhelming ability for these robots to easily perform repetitive lifting greatly improves operator safety, and various gripper options and flexible regrip/orientation stations make difficult positioning simple during the bending sequence as well, offering higher productivity and better profitability.
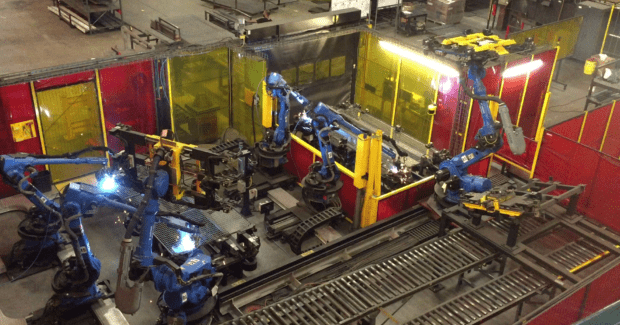
- Material Handling Automation within Robotic Welding Applications. Just as increased robot speed capabilities can reduce air cut time for a welding robot, the combined use of material handling robots or cobots alongside welding robots can streamline production, especially for mid- to high-volume welding applications. A handling robot can move parts from fixture to fixture, loading or unloading weldments, while a welding robot welds parts at another station. This can add much needed flexibility on the production process as well.
- Palletizing Heavy Components on the Factory Floor. No matter the industry – pharmaceuticals, automotive, consumer products and more – consistency and efficiency are important. Heavy-duty robots, like those for loading pallets, can easily move bags, boxes and other containers throughout the factory, easing worker strain and optimizing production process.
- Human-Collaborative Robots for Safe, Efficient Operations. With the shift from centralized manufacturing facilities to distributed manufacturing systems (DMS), the use of human-collaborative robots is gaining popularity, enabling companies to experience greater flexibility in production processes while lowering supply chain costs. Designed to work safely with or in close proximity to human workers, cobots can perform a broad range of tasks, such as machine tending, for fast deployment or redeployment on demand. Likewise, the addition of easy teach tools for these machines has allowed shops to streamline robot training for employees, strengthening workforce development initiatives.
https://youtu.be/DJI2XgeTQcQ
FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
While another investment in robotic automation may seem overwhelming to some manufacturers, management should not lose sight of the operational value that can be gained along the way. Companies that strategically plan for robotic automation and invest in worker training can increase throughput, worker satisfaction and more, successfully achieving return on investment (ROI) over a designated payback period, if not sooner. While significant cost savings can occur over the 15- to 20-year (or more) lifespan of a robot, especially with proper routine maintenance, most companies reach ROI within a two-year payback period. Similarly, redefined organization goals and reasonable expectations, along with attainable redeployment strategies, are a key part of this success, and they should not be overlooked.
Proactive companies that embrace technology and prepare for the challenging pace of change in creative ways, especially with robotic automation for material handling, will have the ability to adjust to market demands and thrive. While employers need to be mindful of hiring practices and worker retention throughout the implementation process – offering educational opportunities and unique incentives to maintain employee satisfaction and profitability – more utilization can increase application capabilities, making automation an easy choice for meeting or exceeding end user requirements. Robot manufacturers and qualified integration partners have engineers that work diligently to create customized workcells with multiple stations and high-density robot spacing for the purpose of optimizing operations.
While many factors can greatly impact the cycle time for production output, the use of material handling robots or cobots for various applications, in conjunction with existing automation processes and innovative peripheral technologies, may be the ideal solution for companies looking for an alternative road to productivity and profitability in the year to come.
https://youtu.be/YGjRIEQ1xoM